Problem
Any minor alteration to an embedded system can yield severe consequences. Furthermore, if issues are identified and addressed belatedly, the rectification process becomes highly costly. Hence, it is imperative to have the capability to test each modification to an embedded system swiftly, within minutes. This is the sole method to promptly identify and resolve issues. Consequently, the adoption of the test pyramid becomes crucial in addressing this concern.
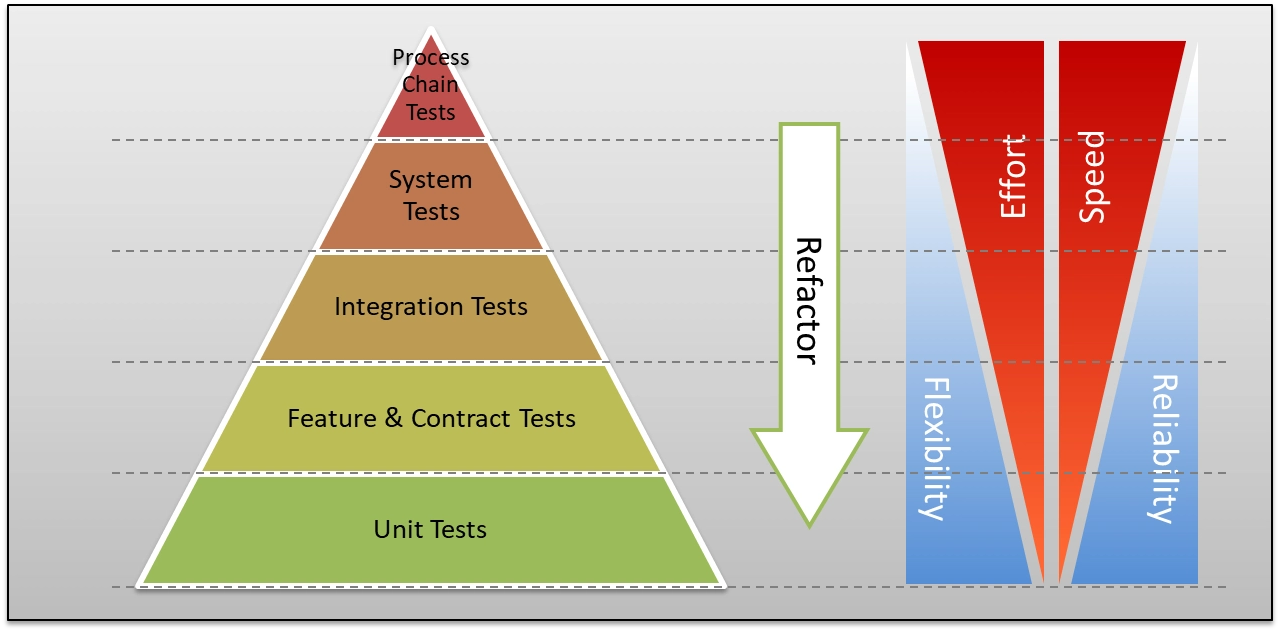
A software system is tested at various levels: unit, integration, system, and acceptance. The test pyramid advocates for a higher number of automated tests at the lower levels (unit and integration) and fewer tests at higher levels (system and acceptance). Unit and integration tests use API-based tools, while system and acceptance tests employ GUI-based tools. The test pyramid aligns with the principle of early QA and testing, aiming to eliminate defects early in the development lifecycle. As we move up the pyramid, testing becomes more expensive.
Continuous Integration for Test Automation
- Developers commit software changes to a central source code management system (e.g., GIT).
- Commits trigger notification to the Continuous Integration (CI) server.
- The CI server checks out changes, rebuilds the software project, and runs automated tests.
- a. If a test fails, the notifying developer is informed (e.g., via email).
- b. If all tests pass, results are logged.
- Complete releases, including documentation and release notes, are built to ensure readiness for automated delivery.
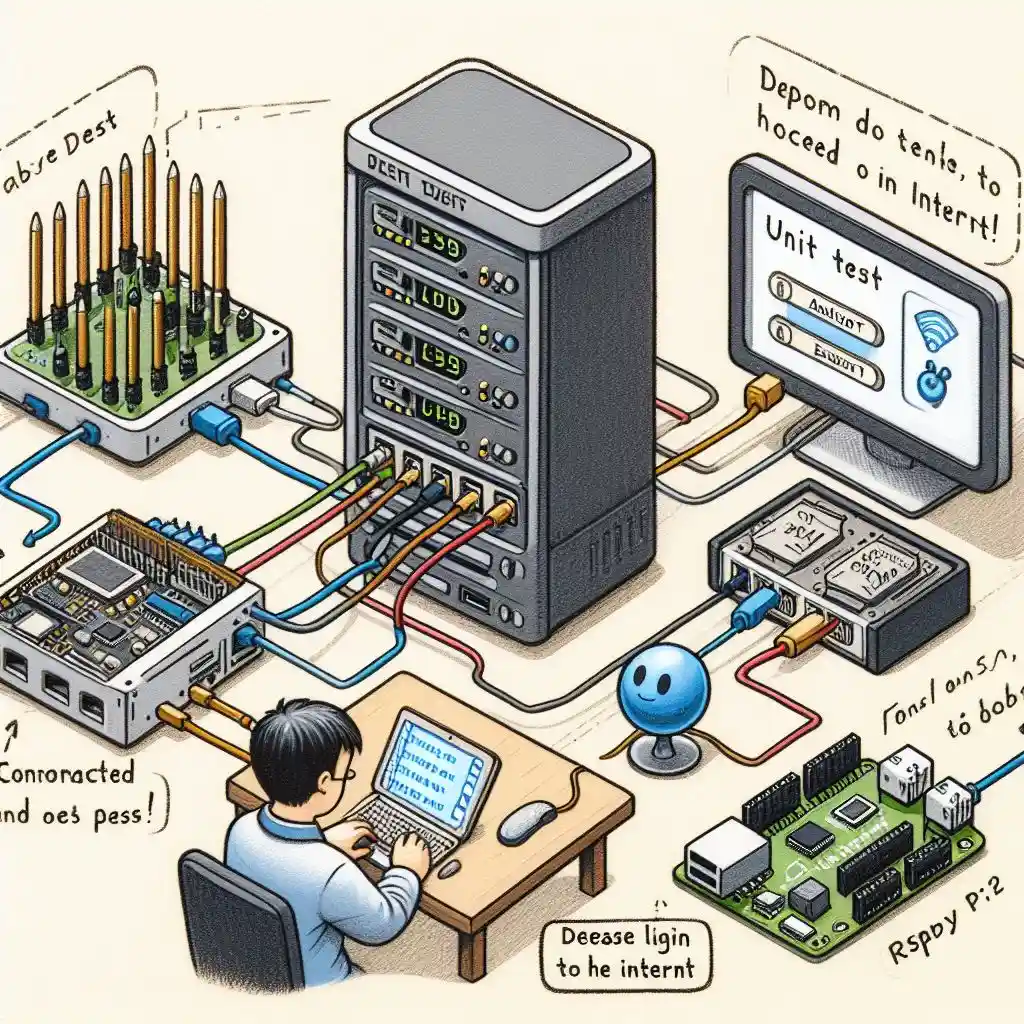
- The challenge in embedded systems is to run tests promptly after each software change, particularly for system or integration tests.
Our Solution
Following standard CI/CD operations, we automate system tests using a dedicated hardware server. This server conducts both unit tests on target hardware and system tests, performing operations such as simulating button presses, checking GPIO status, simulating communication protocols (e.g., UART, RS422, RS485), and conducting performance tests. Test results generate a report displaying metrics like test coverage, code smells, static code analysis, and performance test results